Astrophotography is a fascinating form of photography that captures images of celestial objects such as stars, galaxies, and nebulae. However, taking clear and detailed pictures of these objects can be challenging due to various factors such as light pollution and atmospheric distortion. That's where astrophotography filters come into play. In this blog post, we'll explain the different types of astrophotography filters and how they can improve your images.
What Are Astrophotography Filters?
Astrophotography filters are optical devices that block or pass specific wavelengths of light to enhance the quality of astrophotography images. These filters are used with telescopes and cameras to improve the contrast, color, and clarity of celestial objects. They work by blocking unwanted light such as artificial light pollution, atmospheric distortion, and moonlight. This process allows photographers to capture clearer and more detailed images of the night sky.
Types of Astrophotography Filters
Light Pollution Filters
Light pollution filters are designed to eliminate the effects of artificial light sources such as streetlights, buildings, and cars. These filters work by blocking certain wavelengths of light that are commonly found in urban areas. By using a light pollution filter, you can enhance the contrast of your astrophotography, improve the color balance, and reduce the overall noise in your images.
Narrowband Filters Narrowband filters are designed to block specific wavelengths of light while allowing other wavelengths to pass through. This type of filter is ideal for capturing deep-sky objects such as galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters. By blocking certain wavelengths of light, narrowband filters allow photographers to capture images of these objects that would be impossible to capture with other filters.
Narrowband Filters
Narrowband filters are used to capture images of specific objects such as nebulae and gas clouds. These filters block all light except for a narrow band of wavelengths emitted by the target object. This process enhances the contrast of the object against the dark background of space, making it stand out in the image. Narrowband filters come in different varieties, such as hydrogen-alpha (Ha) filters, oxygen III (OIII) filters, and sulfur II (SII) filters, each designed to capture a specific wavelength of light.
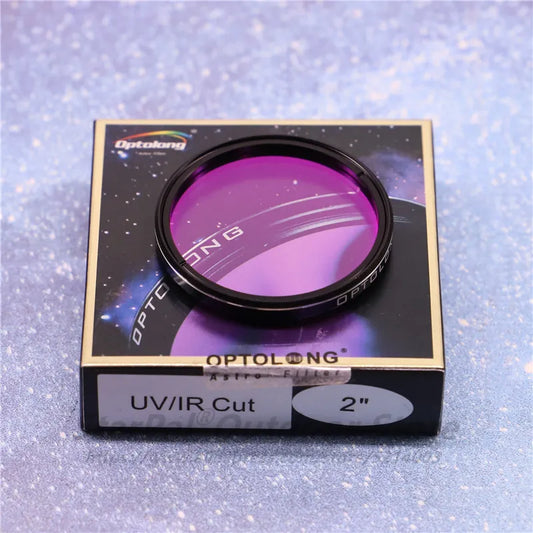
UV/IR Cut Filters
UV/IR cut filters are designed to eliminate the effects of ultraviolet and infrared radiation. These filters are essential for astrophotography because ultraviolet and infrared radiation can cause color shifts, vignetting, and other image quality issues. By using a UV/IR cut filter, you can achieve more accurate colors and sharper images.
Color Filters
Color filters are designed to enhance the color of your astrophotography. These filters work by blocking certain colors of light and allowing other colors to pass through. By using a color filter, you can enhance the colors of the stars, planets, and other celestial objects in your images.
Polarizing Filters Polarizing filters are designed to eliminate glare and reflection from non-metallic surfaces. These filters are not commonly used in astrophotography, but they can be useful for capturing images of the moon or other reflective objects.
Gradient Filters
Gradient filters are designed to balance the exposure of your astrophotography. These filters are particularly useful for capturing images of the moon or other bright objects in the night sky. By using a gradient filter, you can ensure that the exposure of your image is balanced and that the details of the object are visible.
Infrared Filters Infrared filters are designed to block visible light and allow only infrared light to pass through. These filters are not commonly used in astrophotography, but they can be useful for capturing images of the moon or other objects that emit infrared radiation.
H-Alpha Filters
H-Alpha filters are designed to capture images of hydrogen-alpha emission nebulae. These filters work by allowing only a narrow band of light to pass through, which is emitted by hydrogen-alpha emission nebulae. By using an H-Alpha filter, you can capture stunning images of these nebulae and enhance the contrast of your astrophotography.
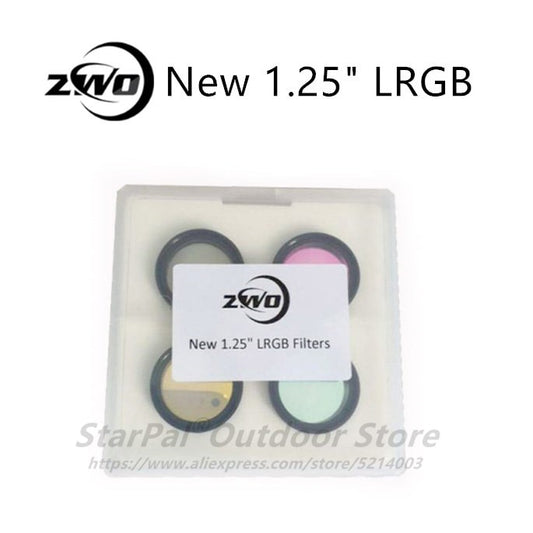
LRGB Filters
LRGB filters are a combination of four different filters: Luminance, Red, Green, and Blue. These filters are designed to capture the full color spectrum of the night sky. By using an LRGB filter, you can capture stunning images of the stars, planets, and other celestial objects in your images.
Moon Filters
Moon filters are designed to reduce the brightness of the moon and enhance the contrast of your astrophotography. These filters are particularly useful for capturing images of the moon.
Choosing the Right Astrophotography Filter
Choosing the right astrophotography filter depends on the object you want to photograph and the conditions in which you are shooting. If you're shooting in an area with heavy light pollution, a light pollution filter is essential. If you want to capture specific objects such as nebulae and gas clouds, a narrowband filter will be necessary. For general astrophotography, a UV/IR cut filter will improve the image's clarity and sharpness.
Conclusion
Astrophotography filters are essential tools for any astrophotographer. They enhance the quality of images by blocking unwanted light and improving contrast, color, and clarity. By understanding the different types of astrophotography filters and their uses, you can improve your astrophotography skills and capture stunning images of the night sky. Remember, the key to successful astrophotography is patience, practice, and the right equipment.
More Light Pollution and Filters Topics:
- What Filters do I need for Astrophotography
- Top 10 Best Filters for Astrophotography
- Hydrogen Alpha Filter
- Optolong l-Pro vs l-Enhance vs l-Extreme
- Planetary Filters
- Solar Telescope Filters
- Best Filter for Galaxies
- ND Filter for Astrophotography
- Light Pollution Filters for Telescope
- Light Pollution Filter for DSLR
- Astrophotography Filter Drawer
- How to put a Filter on a Telescope
- Best Light Pollution Filter for DSLR Astrophotography
- How does Light Pollution affect the visibility of Stars
- Light Pollution Definition
- Do Light Pollution Filters work
- Light Pollution Filter Astrophotography