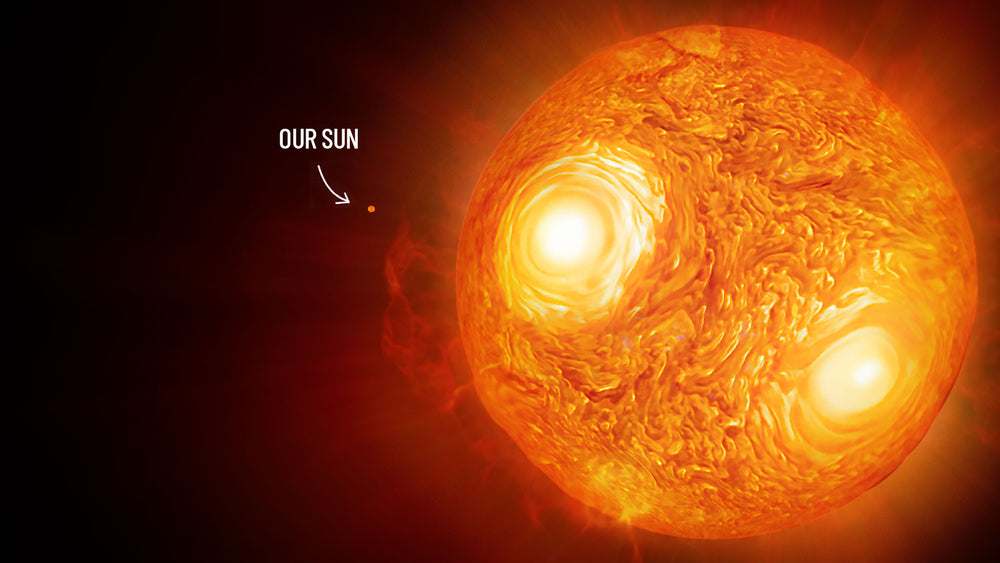
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, celestial bodies come in all shapes and sizes, each with its own unique characteristics that make it a fascinating subject of study. In this comparison, we delve into the differences between three intriguing objects: UY Scuti, the Sun, and Phoenix A. Let's explore the realms of these giants and understand what sets them apart.
Phoenix A vs UY Scuti vs Sun
In a nutshell, UY Scuti, the Sun, and Phoenix A represent a trio of remarkable celestial objects with distinct characteristics:
- UY Scuti stands out for its colossal size, challenging our notions of star dimensions. As a red supergiant, it offers insights into massive star evolution and the intricate interplay of forces within these celestial giants.
- The Sun, our very own star, may seem ordinary, but its stability and proximity have made it a crucial object of study. It powers our solar system, influencing planetary orbits and fostering life on Earth.
- Phoenix A, a distant radio galaxy, showcases the dramatic interaction between supermassive black holes and galaxies. Its emissions provide a glimpse into the cosmic processes shaping the evolution of galaxies.
These stellar wonders broaden our understanding of the universe, offering windows into stellar evolution, energy production, and the dynamic interplay of cosmic forces.
Sun vs Phoenix A vs UY Scuti - Comparison Table
Here's a detailed specification table comparing UY Scuti, the Sun, and Phoenix A:
| Property | UY Scuti | Sun | Phoenix A |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Red Supergiant Star | G-type Main Sequence Star | Radio Galaxy |
| Size | Diameter: Approx. 1,700 times that of Sun | Diameter: Approx. 109 times that of Earth | Varies; Size of entire galaxy |
| Mass | Est. 7 - 10 Solar Masses | Approx. 333,000 Earth Masses | Varies; Mass of the central black hole |
| Temperature | Surface: Est. 3,000 - 3,500°C | Core: Approx. 15 million°C | Emission: Varies with distance |
| Distance from Earth | Est. 9,500 - 9,600 light-years | Approx. 93 million miles (1 AU) | Varies; Typically billions of light-years |
| Characteristics | One of the largest known stars | Powers our solar system | Radio emissions from supermassive black hole |
| Significance | Offers insights into red supergiant evolution | Essential for life on Earth | Helps understand galaxy evolution |
UY Scuti

UY Scuti is a colossal red supergiant star, captivating astronomers with its enormous size. With a diameter of around 1,700 times that of the Sun, it holds the title of one of the largest known stars in the universe. Located about 9,500 - 9,600 light-years away, its surface temperature ranges from 3,000 to 3,500 degrees Celsius. This mammoth star offers valuable insights into the evolution of red supergiants and their eventual fate.
Sun

The Sun, our home star, is a G-type main sequence star that plays a pivotal role in sustaining life on Earth. With a diameter of approximately 109 times that of Earth, the Sun's core temperature reaches a staggering 15 million degrees Celsius. It radiates vital energy that powers our solar system, providing warmth, light, and the necessary conditions for life to flourish on our planet.
Phoenix A

Phoenix A stands out as a radio galaxy, distinct from the realm of individual stars. It defies traditional size measurements, as it encompasses the dimensions of an entire galaxy. Notable for its central supermassive black hole, this galaxy emits powerful radio emissions that enable astronomers to study distant celestial phenomena. Positioned billions of light-years away, Phoenix A aids our understanding of galaxy evolution and the cosmic forces shaping our universe.
Size Comparison
- UY Scuti: As one of the largest known stars, UY Scuti holds the title of being a red supergiant with an estimated radius of up to 1,700 times that of the Sun. Its colossal size highlights the incredible diversity in stellar dimensions.
- Sun: Our very own Sun, a G-type main-sequence star, has a diameter of about 1.4 million kilometers. Despite its relatively modest size compared to giants like UY Scuti, the Sun plays a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth.
- Phoenix A: Phoenix A, a powerful radio galaxy, refers to the radio source associated with the remnant of a supermassive black hole. While not as physically large as UY Scuti, its emissions and impact on its surroundings make it an astronomical wonder.
Diameter Comparison
- UY Scuti: With its astounding size, UY Scuti dwarfs even the largest stars like Betelgeuse. Its immense diameter contributes to its luminosity and evolutionary path.
- Sun: The Sun's diameter, although not among the largest in the cosmos, is substantial enough to support the solar system and provide the energy required for life on Earth.
- Phoenix A: As a radio galaxy, Phoenix A's diameter is associated with the scale of its radio emissions and the remnants of its supermassive black hole.
Mass Comparison
- UY Scuti: While its mass is still debated, UY Scuti's estimated mass could be anywhere from 7 to 10 times that of the Sun. This red supergiant showcases the variability of stellar masses.
- Sun: The Sun's mass, at approximately 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms, is used as a benchmark to measure the masses of other celestial bodies.
- Phoenix A: The mass of the supermassive black hole within Phoenix A is significant, likely in the millions to billions of solar masses, making it an influential force in its galaxy.
Temperature Comparison
- UY Scuti: As a red supergiant, UY Scuti has a surface temperature significantly cooler than that of the Sun, emitting its energy in the form of infrared radiation.
- Sun: The Sun's core temperature reaches around 15 million degrees Celsius, generating the fusion reactions that sustain its energy output.
- Phoenix A: The temperature of the supermassive black hole in Phoenix A's core is incredibly high due to the intense gravitational forces involved.
Distance from Earth Comparison
- UY Scuti: UY Scuti is situated around 9,500 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Scutum, making it relatively close in astronomical terms.
- Sun: The Sun is our nearest star, located approximately 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) away from Earth.
- Phoenix A: This radio galaxy is located in the constellation Phoenix and is much farther away from Earth, estimated to be around 1.2 billion light-years distant.
Luminosity and Evolution
- UY Scuti: Due to its immense size, UY Scuti shines with remarkable luminosity. It undergoes a complex cycle of fusion reactions, resulting in the synthesis of heavier elements and the eventual transformation into a supernova or a planetary nebula.
- Sun: The Sun's luminosity is vital for Earth's climate and habitability. Its fusion reactions in the core provide a steady stream of energy that fuels everything from photosynthesis to weather patterns.
- Phoenix A: This radio galaxy's luminosity is primarily in the radio frequency range, emitted from the vicinity of its supermassive black hole. Its emissions offer insights into the powerful processes occurring near these massive cosmic structures.
Astrophysical Implications
- UY Scuti: The study of UY Scuti provides valuable insights into the late stages of stellar evolution, helping astronomers understand the fate of massive stars and the elements they produce.
- Sun: The Sun's predictable behavior is crucial for Earth's habitability and has allowed scientists to study stellar processes up close, enabling a deeper understanding of stars' lifecycles.
- Phoenix A: As a radio galaxy, Phoenix A's emissions reveal the presence of supermassive black holes in distant galaxies. These black holes have a significant impact on their surrounding environments.
Significance in Cosmology
- UY Scuti: UY Scuti's massive size exemplifies the incredible diversity of stars and challenges our understanding of stellar evolution and their potential impacts on the galaxy.
- Sun: The Sun's stability and energy output have fostered life on Earth, making it a cornerstone of our solar system's dynamics and the study of habitable planets.
- Phoenix A: The presence of supermassive black holes, such as the one in Phoenix A, offers a window into the active and energetic processes occurring in the centers of galaxies, shaping their evolution.
Astronomical Exploration
- UY Scuti: Observing UY Scuti and its variations in brightness provides astronomers with insights into the complex processes occurring within massive stars.
- Sun: The Sun's detailed observations and its impact on our planet's environment have led to advancements in solar physics and the understanding of space weather.
- Phoenix A: Studying radio galaxies like Phoenix A helps astronomers uncover the role of supermassive black holes in the evolution of galaxies and the broader universe.
Structural Marvels
- UY Scuti: The sheer enormity of UY Scuti challenges our comprehension. Its size prompts us to question the limits of stellar existence and the dynamics of extreme mass.
- Sun: Our Sun, an ordinary yet vital star, serves as the cornerstone of our solar system. Its relatively stable behavior sustains life on Earth and facilitates studies of stars' fundamental properties.
- Phoenix A: This distant radio galaxy reveals the power of supermassive black holes, influencing galaxies' evolution and shaping the cosmos on a grand scale.
Life Cycles and Evolution
- UY Scuti: UY Scuti's journey to eventual supernova or planetary nebula holds the key to the universe's evolving nature and the creation of elements essential for life.
- Sun: As the nurturing force behind our planet's habitability, the Sun's fusion reactions and energy output sustain life and drive Earth's climate systems.
- Phoenix A: Radio galaxies like Phoenix A remind us of the dynamic and transformative forces at work within galaxies, including the growth and activity of black holes.
Cosmic Context and Exploration
- UY Scuti: Studying UY Scuti expands our knowledge of stellar variability and the complex processes that govern the lives of massive stars.
- Sun: The Sun's study enables us to understand the nature of other stars, their energy production, and their potential impact on their surrounding environments.
- Phoenix A: Radio galaxies like Phoenix A illuminate the interplay between massive black holes and their host galaxies, offering insights into cosmic evolution.
Eyes on the Universe
- UY Scuti: Astronomers focus their instruments on UY Scuti to gain insights into the roles of massive stars in the formation and evolution of galaxies.
- Sun: The Sun, easily observed from Earth, allows scientists to study solar phenomena and their effects on our technologically dependent society.
- Phoenix A: The emissions from radio galaxies like Phoenix A provide astronomers with clues about the energetic processes near supermassive black holes.
In conclusion, the comparison between UY Scuti, the Sun, and Phoenix A underscores the incredible diversity and magnificence of the universe. From the colossal size of UY Scuti to the nurturing warmth of the Sun and the enigmatic nature of Phoenix A, each object contributes to our understanding of the cosmos in its own unique way.