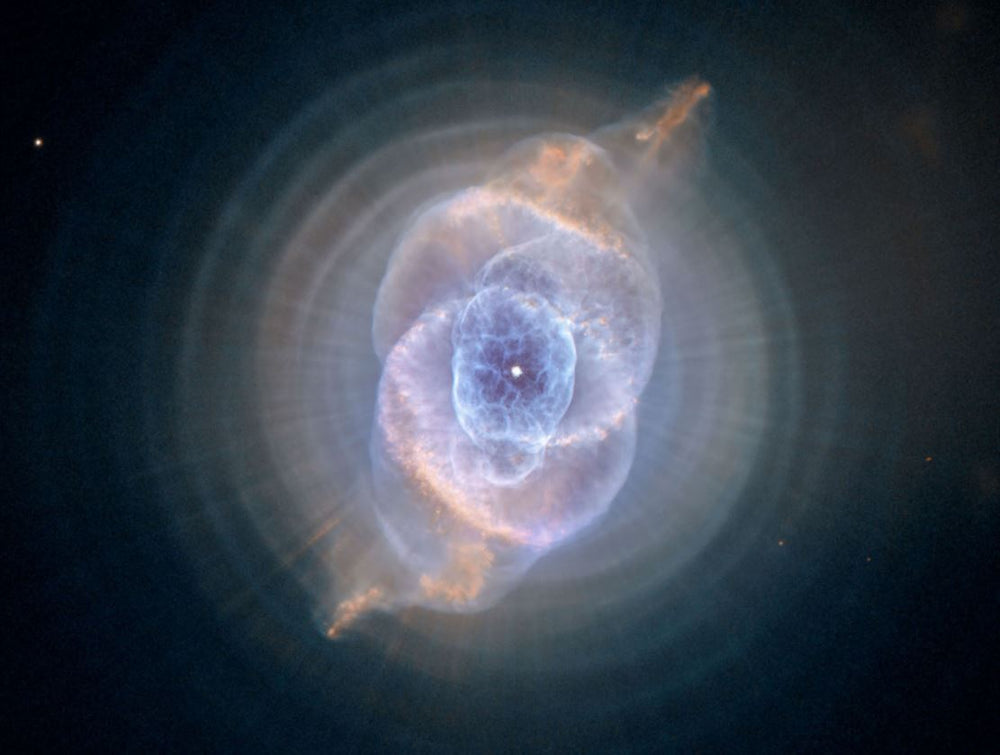
The Cat's Eye Nebula: NGC 6543
The Cat Eye Nebula, also known as NGC 6543, is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Draco. It is a popular subject among astronomers and amateur stargazers due to its unique and striking appearance. In this blog post, we will explore the Cat's Eye Nebula in detail, including its history, structure, and significance in the universe.
NGC 6543 The Cat's Eye Nebula Size in Light Years
The Cat's Eye Nebula, cataloged as NGC 6543, spans an estimated diameter of approximately 0.4 light-years. This compact yet intricate planetary nebula showcases the final stages of a Sun-like star's evolution.
NGC 6543 The Cat's Eye Nebula Apparent / Angular Size
When observed from Earth, the apparent or angular size of the Cat's Eye Nebula is approximately 16 arcseconds by 25 arcseconds. This relatively small size requires the use of telescopes to appreciate the details of its structure.
NGC 6543 The Cat's Eye Nebula Location in Milky Way
NGC 6543, the Cat's Eye Nebula, is located in the constellation Draco within the Milky Way galaxy. Its celestial coordinates place it at a considerable distance from Earth, allowing astronomers to study it within the context of our galactic neighborhood.
NGC 6543 The Cat's Eye Nebula Distance From Earth in Miles / Km / Light Years
The Cat's Eye Nebula is situated at a distance of approximately 3,262 light-years from Earth. This corresponds to roughly 1.9 × 10^16 miles or 3.1 × 10^16 kilometers.
NGC 6543 The Cat's Eye Nebula Star Forming Region
Unlike some other types of nebulae, the Cat's Eye Nebula is not a region where new stars are actively forming. Instead, it is classified as a planetary nebula, representing the final stages of a Sun-like star's life. The central star in the Cat's Eye Nebula has exhausted its nuclear fuel and is in the process of shedding its outer layers.
NGC 6543 The Cat's Eye Nebula Stars Names
The central star of the Cat's Eye Nebula, responsible for illuminating and shaping the surrounding nebula, is referred to as the central star of NGC 6543. The names of individual stars within planetary nebulae are often designated based on the cataloging system rather than specific names.
10 Interesting Fun Facts About NGC 6543 Cat's Eye Nebula
- Stellar Remnants: The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula formed from the outer layers of a dying star expelled into space. The remaining core, known as a white dwarf, is visible at the nebula's center.
- Central Star Temperature: The central star of NGC 6543 is an extremely hot white dwarf with a surface temperature exceeding 100,000 degrees Celsius (180,032 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Complex Structures: The nebula displays intricate structures, including concentric shells, jets, and filaments, which have been shaped by the interactions between the central star and the expelled material.
- Observational Challenges: The Cat's Eye Nebula's small apparent size poses challenges for ground-based telescopes, making it an ideal target for space-based observatories like the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Evolutionary Stage: As a planetary nebula, NGC 6543 represents a transitional phase in the life cycle of a star, marking the end of its red giant phase and the beginning of its transformation into a white dwarf.
- Colorful Emissions: The colors observed in the Cat's Eye Nebula are indicative of various ionized elements, with emissions from hydrogen (red) and oxygen (blue-green) contributing to its vibrant appearance.
- Hubble's Gaze: The Hubble Space Telescope has captured stunning images of the Cat's Eye Nebula, revealing intricate details and providing valuable insights into its structure and composition.
- Expanding Shell: The expelled material from the central star forms a spherical shell expanding outward at a velocity of approximately 1,500 kilometers per second (932 miles per second).
- Interaction with Interstellar Medium: The fast-moving shell of gas and dust from the Cat's Eye Nebula interacts with the surrounding interstellar medium, contributing to the enrichment of the galaxy.
- Scientific Importance: Studying planetary nebulae like NGC 6543 helps astronomers understand the chemical enrichment of the cosmos, the mechanisms of mass loss in dying stars, and the impact of such events on the surrounding galactic environment.
Cat's Eye Nebula Discovery
The Cat's Eye Nebula was first discovered by the British astronomer William Herschel in 1786. Herschel observed the nebula using his 18.7-inch reflector telescope and described it as "a most singular phaenomenon." However, it wasn't until the 20th century that astronomers began to study the nebula in detail.
The Cat's Eye Nebula, also known as NGC 6543, is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Draco. It is one of the most complex and interesting objects in the universe, attracting the attention of both amateur stargazers and professional astronomers. In this blog post, we will explore the Cat's Eye Nebula in detail, including its location, formation, characteristics, composition, size, distance, and interesting facts.
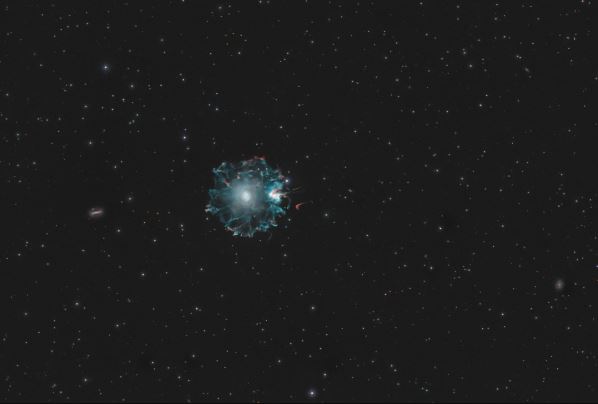

Cat's Eye Nebula Location
The Cat's Eye Nebula is located in the northern constellation of Draco. It is located about 3,000 light-years away from Earth and can be seen in the night sky with a telescope. The nebula was first discovered by William Herschel in 1786 and has since become a popular object of study for astronomers.
Cat's Eye Nebula Formation
The Cat's Eye Nebula was formed from the ejected outer layers of a dying star. When a star like our Sun reaches the end of its life, it undergoes a process called a planetary nebula phase. During this phase, the outer layers of the star are ejected into space, forming a shell around the central core. The intense radiation from the core illuminates the ejected gas, creating the distinctive glow of a planetary nebula. The Cat's Eye Nebula is a prime example of a planetary nebula.

Cat's Eye Nebula Characteristics
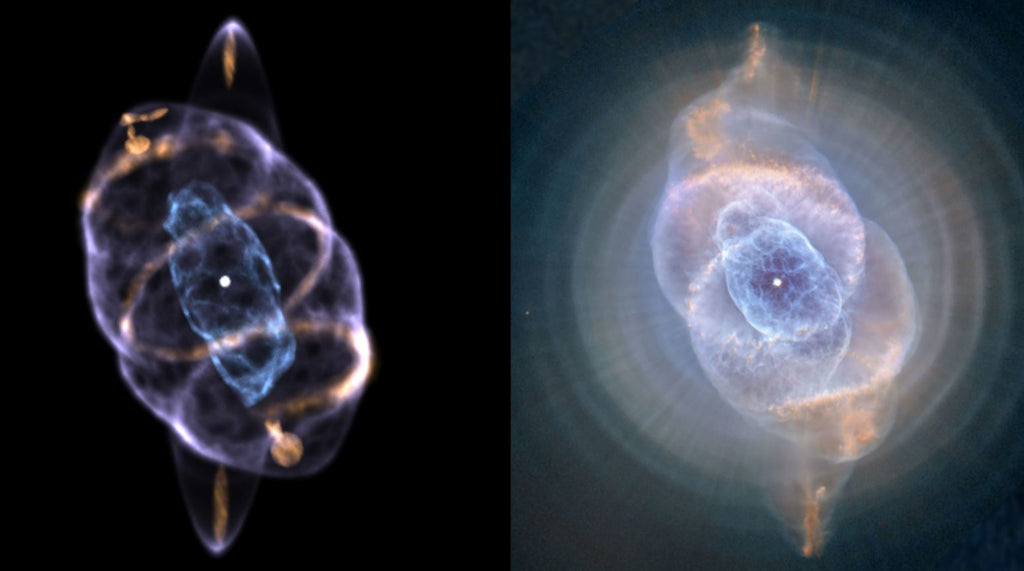
The Cat's Eye Nebula is known for its unique and intricate structure. It consists of a central star, which is a white dwarf, surrounded by a series of concentric shells of gas and dust. These shells are the result of multiple ejections of material from the central star. The nebula also has a faint, spherical region of gas that surrounds the central star, called the halo. In addition, the Cat's Eye Nebula has a series of dark lanes that crisscross the central region of the nebula, which are the result of the interaction between the nebula's gas and dust and the magnetic fields that surround the central star.
Cat's Eye Nebula Composition
The Cats Eye Nebula is composed mainly of hydrogen and helium gas, with small amounts of other elements such as nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon. These elements were created by nuclear fusion within the star before it ejected its outer layers. The composition of the nebula provides valuable insights into the processes that occur during the late stages of stellar evolution.
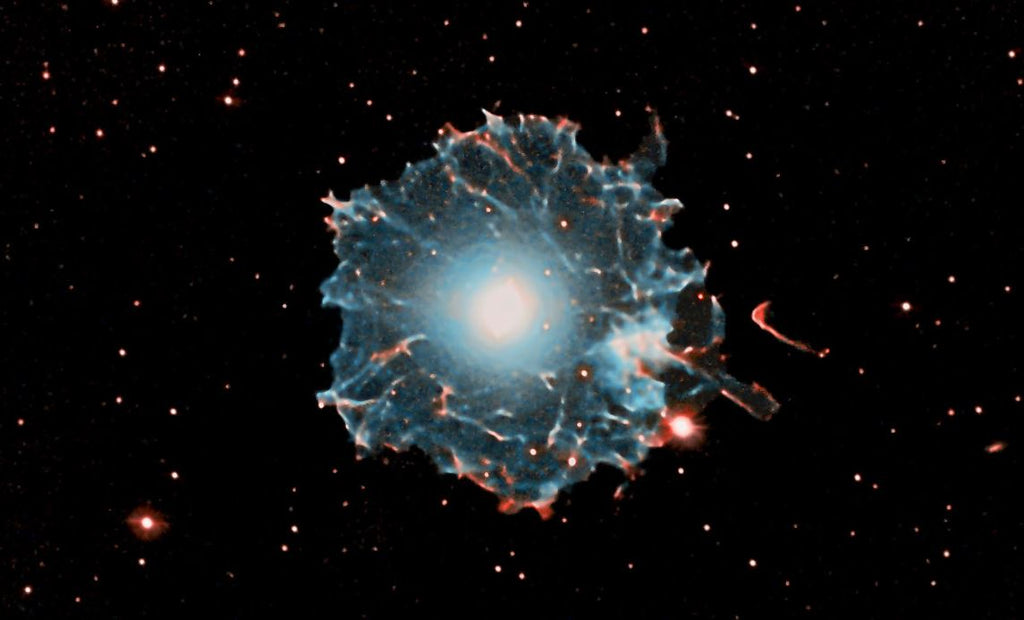

Cat's Eye Nebula Size
The Cat Eye Nebula has a diameter of about 0.4 light-years, which is equivalent to about 2,209,854,800,000 miles. This makes it relatively small compared to other planetary nebulae. However, the intricate structure of the nebula makes it a fascinating object of study for astronomers.
Cat's Eye Nebula Distance
The Cat's Eye Nebula is located about 3,000 light-years away from Earth. This means that the light we see from the nebula today actually left the nebula 3,000 years ago. Studying objects like the Cat's Eye Nebula helps astronomers learn more about the history and evolution of the universe.
Cat's Eye Nebula Facts
- The Cat's Eye Nebula was named after its distinctive appearance, which resembles a cat's eye.
- The central star of the Cat's Eye Nebula is a white dwarf, which is the remnant of a star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel and collapsed under its own weight.
- The Cats Eye Nebula is one of the most complex and well-studied planetary nebulae known to exist.
- The dark lanes that crisscross the Cat's Eye Nebula are thought to be the result of the interaction between the magnetic fields surrounding the central star and the nebula's gas and dust.
- The Cat's Eye Nebula is believed to be one of the youngest planetary nebulae known to exist, with an estimated age of only 1,000 years.
- The Cat Eye Nebula was the subject of the Hubble Space Telescope's 20th-anniversary image, which captured its intricate structure in stunning detail.
- The Cat's Eye Nebula is one of the most popular targets for amateur astronomers, due to its unique appearance and relatively easy visibility in the night sky.
- The Cat Eye Nebula has been studied extensively in various wavelengths of light, including visible light, ultraviolet, and X-rays.
- The Cats Eye Nebula is located in the same region of space as several other well-known objects, including the Draco Dwarf Galaxy and the open cluster NGC 6633.
- Studying the Cat Eye Nebula can provide insights into the evolution of stars and the formation of elements that make up the building blocks of life.
Cat's Eye Nebula Structure
The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula, which means that it is a cloud of gas and dust that has been ejected from a dying star. The nebula is located approximately 3,000 light-years from Earth and has a diameter of about 0.4 light-years. It is one of the most complex planetary nebulae known to exist, with a variety of features that have puzzled astronomers for decades.
One of the most prominent features of the Cat's Eye Nebula is its central star, which is a white dwarf. This star is the remnant of the original star that formed the nebula and is now in the final stages of its life. The white dwarf is surrounded by a series of concentric shells of gas and dust, which give the nebula its distinctive appearance.
Another feature of the Cat Eye Nebula is its halo, which is a faint, spherical region of gas that surrounds the central star. The halo is thought to have formed as a result of the star's intense ultraviolet radiation, which ionized the gas and caused it to expand outward.
In addition to the halo, the Cat Eye Nebula also has a series of dark lanes that crisscross the central region of the nebula. These lanes are thought to be the result of the interaction between the nebula's gas and dust and the magnetic fields that surround the central star.
Scientific Significance
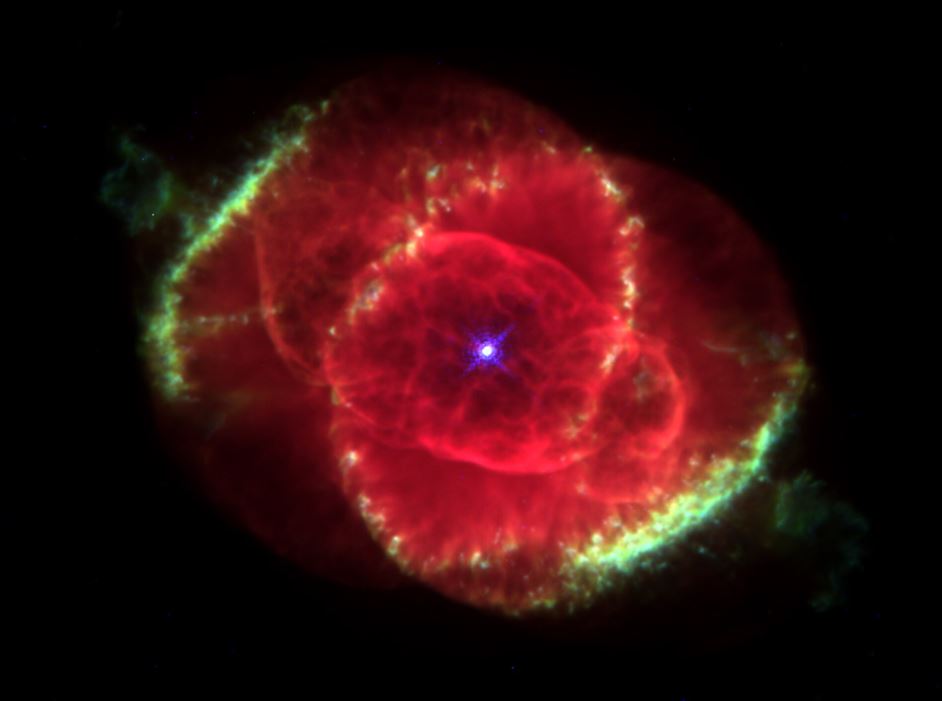
The Cat's Eye Nebula is an important object of study for astronomers because it provides valuable insights into the late stages of stellar evolution. As a planetary nebula, it represents the final phase in the life of a star before it becomes a white dwarf. By studying the nebula's structure and composition, astronomers can learn more about the processes that occur during this phase and how they contribute to the evolution of the universe.
One of the most interesting things about the Cat's Eye Nebula is its complex structure. The concentric shells of gas and dust that surround the central star are thought to have formed as a result of a series of eruptions that occurred over a period of several thousand years. By studying these shells, astronomers can learn more about the processes that drive these eruptions and how they contribute to the evolution of planetary nebulae.
Another important aspect of the Cat Eye Nebula is its chemical composition. The nebula contains a variety of elements, including helium, nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon, which are the building blocks of life. By studying the chemical composition of the nebula, astronomers can learn more about the processes that contribute to the formation of these elements and how they are distributed throughout the universe.

Cat's Eye Nebula
Here is a table describing the main characteristics of the Cat's Eye Nebula:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Cat's Eye Nebula |
| Other names | NGC 6543 |
| Location | Northern constellation of Draco |
| Distance from Earth | Approximately 3,000 light-years |
| Diameter | Approximately 0.4 light-years |
| Age | Estimated to be about 1,000 years old |
| Formation | Formed from ejected outer layers of a dying star |
| Central star | White dwarf, remnant of original star that formed the nebula |
| Structure | Consists of a series of concentric shells of gas and dust |
| Central star is surrounded by a faint spherical region of gas | |
| Nebula also has a series of dark lanes that crisscross the gas | |
| Composition | Mainly composed of hydrogen and helium, with small amounts of |
| other elements such as nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon | |
| Interesting features | Dark lanes are the result of interaction between the nebula's |
| gas and dust and the magnetic fields surrounding the star | |
| One of the most complex and well-studied planetary nebulae | |
| Popular target for amateur astronomers due to its unique | |
| appearance and visibility in the night sky | |
| Significance | Provides valuable insights into the late stages of stellar |
| evolution and the formation of elements that make up the | |
| building blocks of life. |
This table provides a quick overview of the main characteristics of the Cat Eye Nebula, including its location, size, composition, and unique features. It also highlights the significance of studying this object in terms of our understanding of stellar evolution and the formation of elements in the universe.
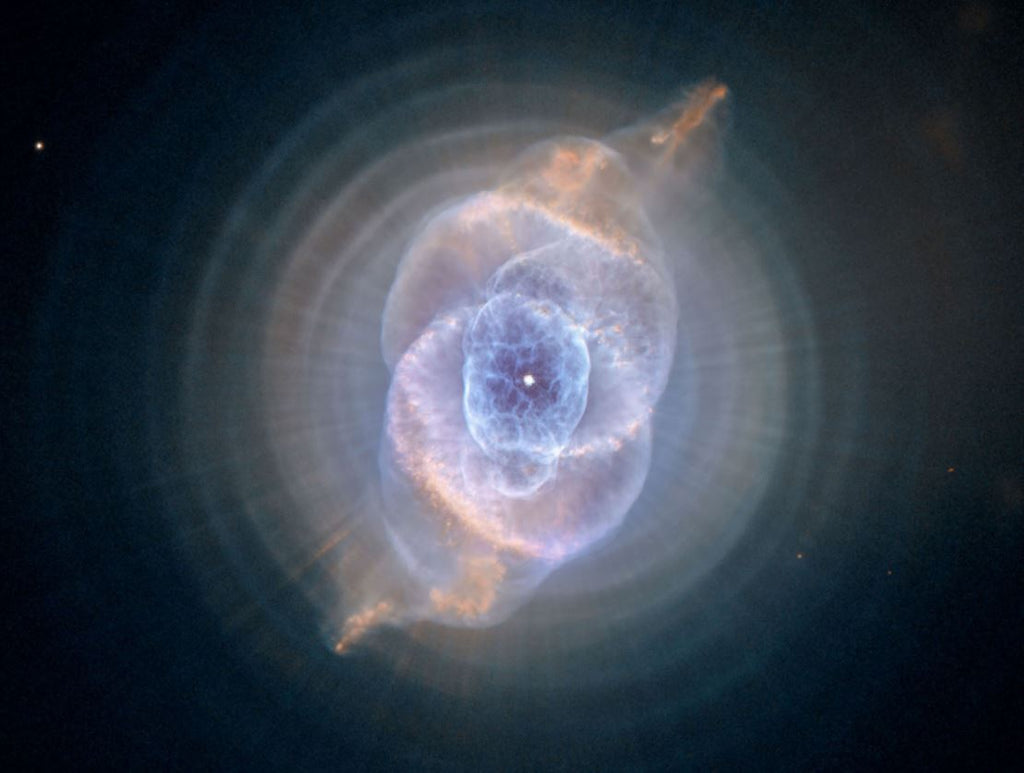

Conclusion
The Cat's Eye Nebula is a fascinating object of study for astronomers and amateur stargazers alike. Its unique and complex structure, as well as its chemical composition, provide valuable insights into the late stages of stellar evolution and the evolution of the universe as a whole. By continuing to study the Cats Eye Nebula, astronomers hope to learn more about the processes that drive the formation and evolution of planetary nebulae, as well as the distribution of elements throughout the universe.
In addition to its scientific significance, the Cats Eye Nebula is also a popular subject for astrophotographers. Its striking appearance and intricate structure make it a favorite among those who seek to capture the beauty of the universe through their cameras.
Overall, the Cat Eye Nebula is a fascinating and important object in the universe. Its complex structure and chemical composition provide valuable insights into the processes that shape our universe and the evolution of stars and planets. As our understanding of the universe continues to grow, the Cat's Eye Nebula will undoubtedly remain a subject of study and fascination for generations to come.
More Nebulas:
- Orion Nebula
- Elephant Trunk Nebula
- California Nebula
- Crab Nebula
- Helix Nebula
- Carina Nebula
- Eagle Nebula
- Ring Nebula
- Horsehead Nebula
- Veil Nebula
- Flaming star Nebula
- Bubble Nebula
- Pelican Nebula
- Tarantula Nebula
- Monkey Head Nebula
- Trifid Nebula
- North American Nebula
- Rosette Nebula
- Jellyfish Nebula
- Lagoon Nebula
- Heart Nebula
- Pacman Nebula
- Witch head Nebula
- Cone Nebula
- Eskimo Nebula
- Iris Nebula
- Omega Nebula
- Swan Nebula
- Cygnus Loop
- Sadr Region
- Barnard's Loop
- Large Magellanic Cloud
- Small Magellanic Cloud
- NGC 1360

